five kinds of non-九游会登录
there are many methods of industrial non-destructive testing, at present, there are five most commonly used testing methods at home and abroad, that is, people often call the five conventional testing methods: x-ray testing, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, eddy current testing and penetration testing.
users should combine their own specific conditions and needs to choose more suitable for the company's inspection products.





1.射线探伤方法

radiographic inspection is a method that uses the penetration and straightness of rays to detect faults. these rays are not directly visible to the naked eye like visible light, but they sensitize photographic plates and can be picked up by special receivers.
x-rays and gamma rays emitted by isotopes are commonly used for flaw detection, called x-ray and gamma ray detection, respectively. when these rays pass through (irradiate) a substance, the greater the density of the substance, the more the intensity of the rays is weakened, that is, the less the intensity of the rays can penetrate the substance. at this time, if the photographic plate is received, the sensitivity of the negative is small; if the instrument is used to receive, the signal obtained is weak.
therefore, when using the ray to irradiate the parts to be detected, if there are defects such as pores and slag inside, the density of the material through the path of the ray passing through the defective path is much smaller than that of the path without defects, and its strength is weakened less, that is, the intensity of the transmission is greater, and if the negative is received, the sensitivity is greater. the plane projection of the defect perpendicular to the ray direction can be reflected from the negative. if other receivers are used, the meter can also be used to reflect the plane projection of the defect perpendicular to the ray direction and the radiation transmission.
由此可见,一般情况下,射线探伤是不易发现裂纹的,或者说,射线探伤对裂纹是不敏感的,因此,射线探伤对气孔、夹渣、未焊透等体积型缺陷最敏感,即射线探伤适宜用于体积型缺陷探伤,而不适宜面积型缺陷探伤,另,射线探伤价格一般较贵。
2. ultrasonic inspection method

the frequency range of sound waves that people's ears can directly receive is usually 20hz to 20khz, that is, the sound (sound) frequency. frequencies below 20hz are called infrasound, and those above 20khz are called ultrasonic. multi-megahertz ultrasound is commonly used in industry for flaw detection.
the ultrasonic frequency is high, the linearity of the propagation is strong, and it is easy to propagate in solids, and it is easy to reflect when encountering the interface formed by two different media, so that it can be used to detect the flaw. usually, with a good contact between the ultrasonic probe and the surface of the workpiece to be explored, the probe can effectively emit ultrasonic waves to the workpiece, and can receive the ultrasonic waves reflected by the (defect) interface, and convert them into electrical signals, and then transmit them to the instrument for processing.
according to the speed of ultrasonic propagation in the medium (often called the speed of sound) and the propagation time, the location of the defect can be known. when the defect is larger, the reflecting surface is larger, and the reflected energy is larger, so the size of each defect (equivalent) can be found according to the size of the reflected energy. common detection waveforms are p-wave, s-wave, surface wave, etc. the former two are suitable for detecting internal defects, and the latter is suitable for detecting surface defects, but the surface conditions are high.
3. magnetic particle detection method

magnetic particle flaw detection is a kind of magnetic flaw detection method based on the principle of magnetic leakage. when the magnetic field line passes through the ferromagnetic material and its products, a leakage magnetic field will be generated at its (magnetic) discontinuity, forming a magnetic pole. at this time, dry magnetic powder is sprinkled or magnetic suspension is poured, and the magnetic pole will adsorb magnetic powder, resulting in obvious magnetic marks that can be directly observed with the naked eye. therefore, the magnetic marks can be used to show the defects of ferromagnetic materials and their products.
the magnetic particle inspection method can detect the exposed surface, with the naked eye or with the aid of a magnifying glass can not be directly observed small defects, but also can detect the surface of the surface is not exposed, but buried a few millimeters below the surface. although this method can also detect porosity, inclusion, non-penetration and other volume defects, it is more sensitive to area defects and more suitable for inspecting cracks caused by quenching, rolling, forging, casting, welding, electroplating, grinding, fatigue and so on.
there are many ways to display defects in magnetic inspection, including magnetic powder display and non-magnetic powder display. the magnetic powder display is called magnetic powder flaw detection, because it is intuitive, simple to operate, and people are willing to use, it is one of the most commonly used methods. without magnetic powder display, it is customary to call magnetic leakage testing, which often reflects the defect by means of induction coils, magnetic tubes, hall elements, etc., which is more hygienic than magnetic powder testing, but not as intuitive as the former.
because the current magnetic flaw detection mainly uses magnetic powder to show defects, people sometimes refer to magnetic particle detection directly as magnetic flaw detection, and its equipment is called magnetic flaw detection equipment. magnetic particle flaw detection is widely used in the detection of automobile engine parts.
4. eddy current inspection method
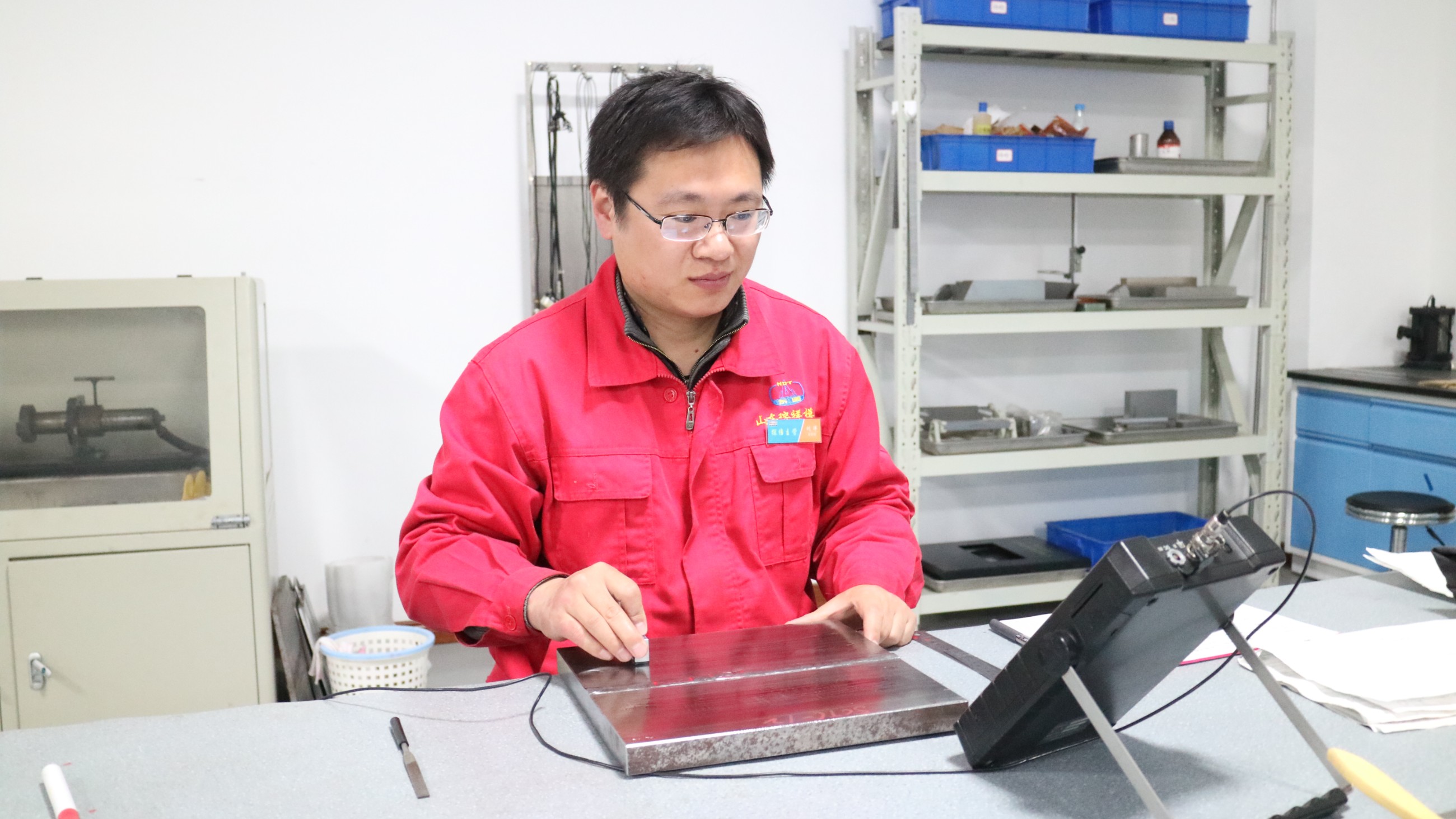
eddy current detection is an alternating magnetic field generated by alternating current acting on the conductive material to be detected and inducing eddy current. if there is a defect in the material, it will interfere with the generated eddy currents, that is, the interference signal is formed. the interference signal can be detected by the eddy current flaw detector, and the condition of the defect can be known.
there are many factors affecting the eddy current, that is, the eddy current contains rich signals, which are related to many factors of the material. how to separate the useful signals from one of the many signals is a difficult problem for current eddy current researchers. some progress has been made over the years, and some problems can be solved under certain conditions, but it is still far from meeting the requirements of the field. it needs to be vigorously developed.
the remarkable feature of eddy current testing is that it can work on conductive materials, not necessarily ferromagnetic materials, but the effect on ferromagnetic materials is poor. secondly, the surface smoothness, flatness and boundary of the workpiece to be explored have a great impact on eddy current testing, so eddy current testing is often used for non-ferromagnetic workpiece detection such as copper pipe with regular shape and smooth surface.
5. penetration detection method

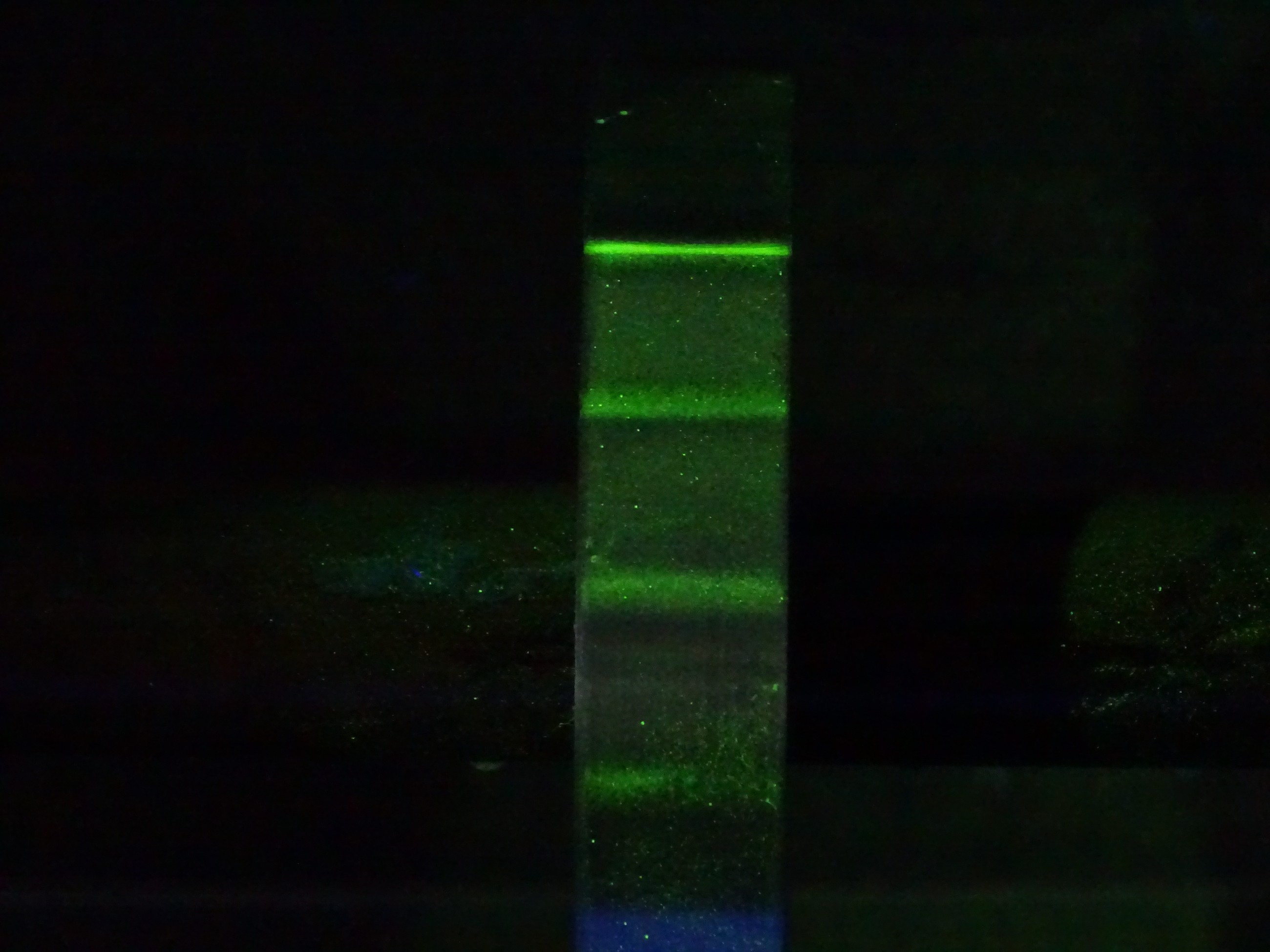
penetration testing is a method of using capillary phenomenon to detect faults. for smooth and clean parts, use a colored (usually red) or fluorescent, highly permeable liquid to coat the surface of the part to be explored.
if there are micro-cracks on the surface that cannot be directly observed by the naked eye, due to the strong permeability of the liquid, it will penetrate along the crack to its root; then wash the surface of the permeating liquid, and then paint the display liquid with large contrast (often white), placed for a moment, because the crack is very narrow, the capillary phenomenon is significant, the original permeating liquid into the crack will rise to the surface and spread, in the white substrate showed a thicker red line, thus showing the shape of the crack exposed to the surface, therefore, often called color detection.
if the osmotic solution is a liquid with fluorescence, the capillary phenomenon rises to the surface of the liquid, it will emit fluorescence under the ultraviolet lamp, so that it can show the shape of the crack exposed to the surface, so often the penetration detection at this time is directly called fluorescence detection. the flaw detection method can also be used for metal and non-metal surface detection, the use of the flaw detection liquid agent has a larger odor, often a certain toxicity.
in addition to the above five conventional methods, in recent years, there are some new flaw detection methods such as infrared and acoustic emission.









